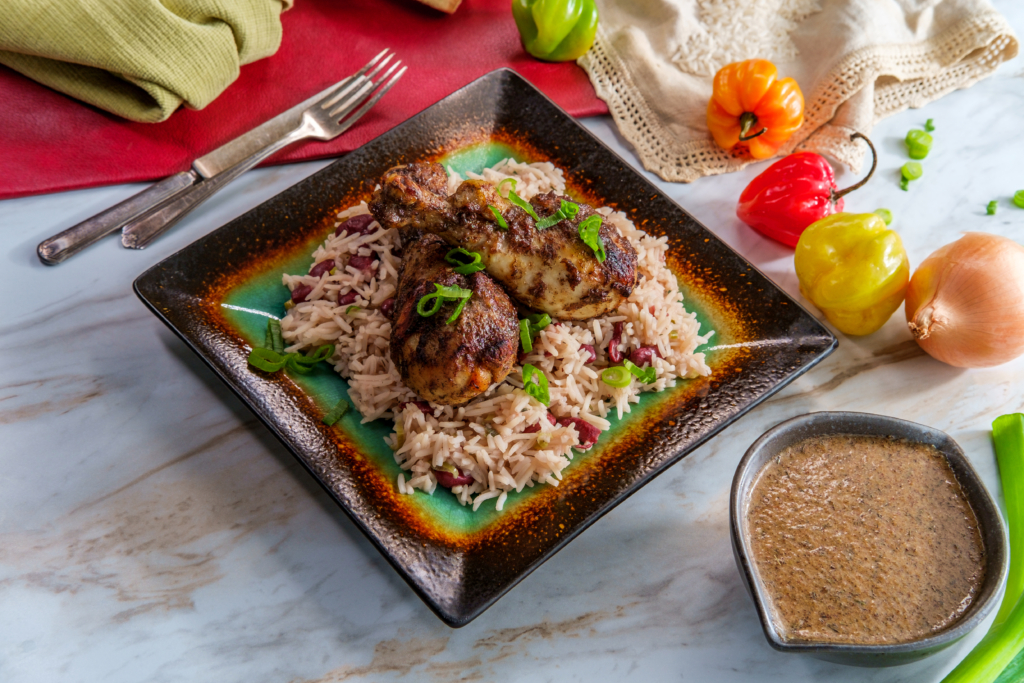
If you have ever enjoyed authentic Jamaican jerk chicken or hot sauce, then you’ve experienced the fruity intensity that is Scotch Bonnet Chile Pepper. It is the chile of choice in the Caribbean area and a staple in Jamaican cuisine. If you think jalapeño peppers are hot, then the Scotch Bonnet Pepper is not for you.

Scorch Your Senses
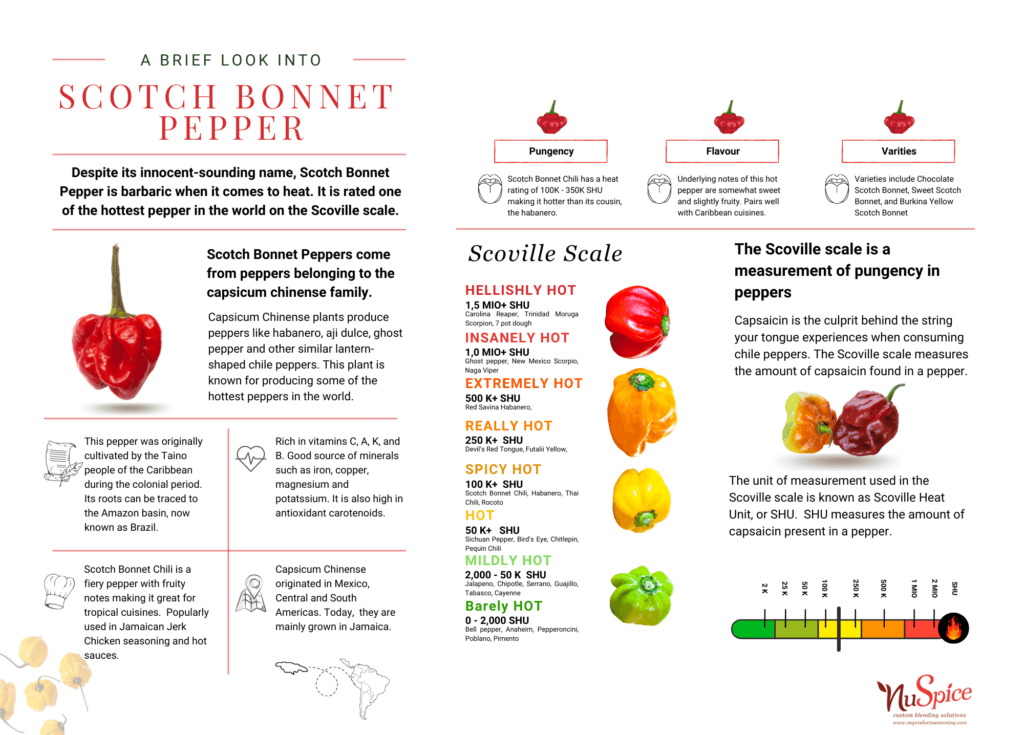
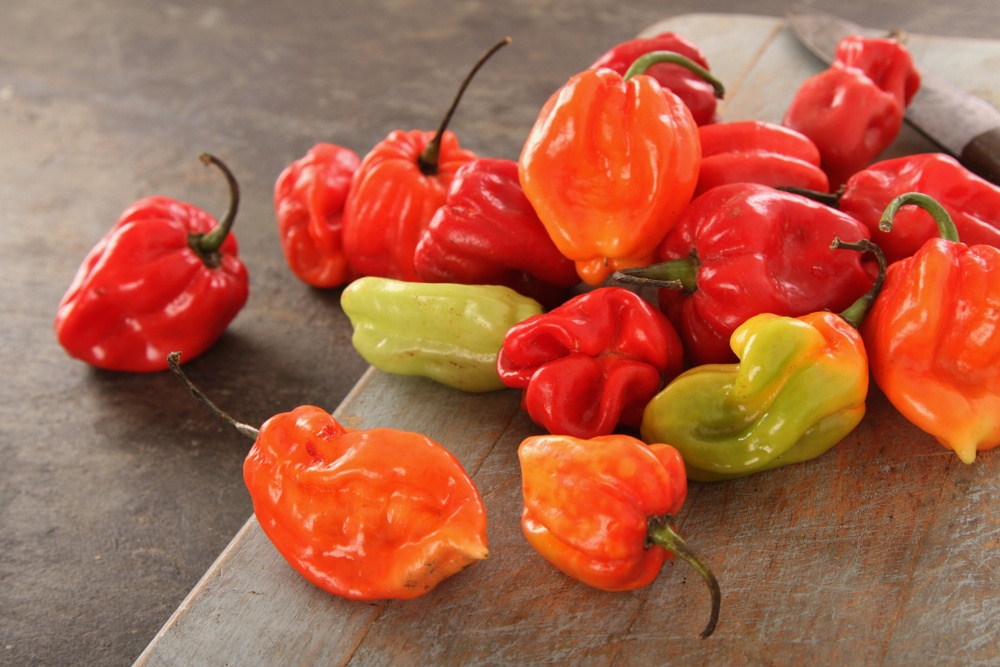
Despite its innocent-sounding name, Scotch Bonnet chili pepper is barbaric when it comes to pungency, or spiciness. Named after its resemblance to a tam o’ shanter hat, this chile pepper belongs to the Capsicum Chinense species. Capsicum Chinense contains some of the world’s hottest pepper, including the infamous Carolina Reaper (1,5mil+ SHU) and the ever-popular ghost pepper (1 mil+ SHU). However, its most recognized chile is the habanero pepper! Most Capsicum Chinense chile peppers vary in appearance, depending on the soil conditions. Some are vibrant red, yellow, green, or even chocolate brown! They are usually short in shape and typically tend to resemble a lantern. Scotch Bonnet Peppers has a heat rating of 100K – 350K SHU.
(SHU stands for Scoville Heat Units which is based on the Scoville scale – the official measurement of pungency in chile peppers)
Spicy Origins
The origins of the Scotch Bonnet pepper are not quite concrete. Species of the Capsicum Chinense are believed to have origins in Mexico, Central and South Americas. Scotch Bonnet peppers can be traced to the Amazon basin, or Brazil. It is here where a subgroup of the Arawakan tribes, the Taino people, first encountered this fruity and fiery pepper. The Taino eventually traveled from present-day Venezuela to the Greater Antilles, transporting animals and plants with them, including the Scotch Bonnet pepper. Unfortunately, the Taino people were wiped out due to disease, enslavement, and massacre (thanks to Columbus) but their food and culture remained with the eventually freed slaves that remained. Today, Jamaica is the main exporter of Scotch Bonnet Peppers.

Spice it Up!
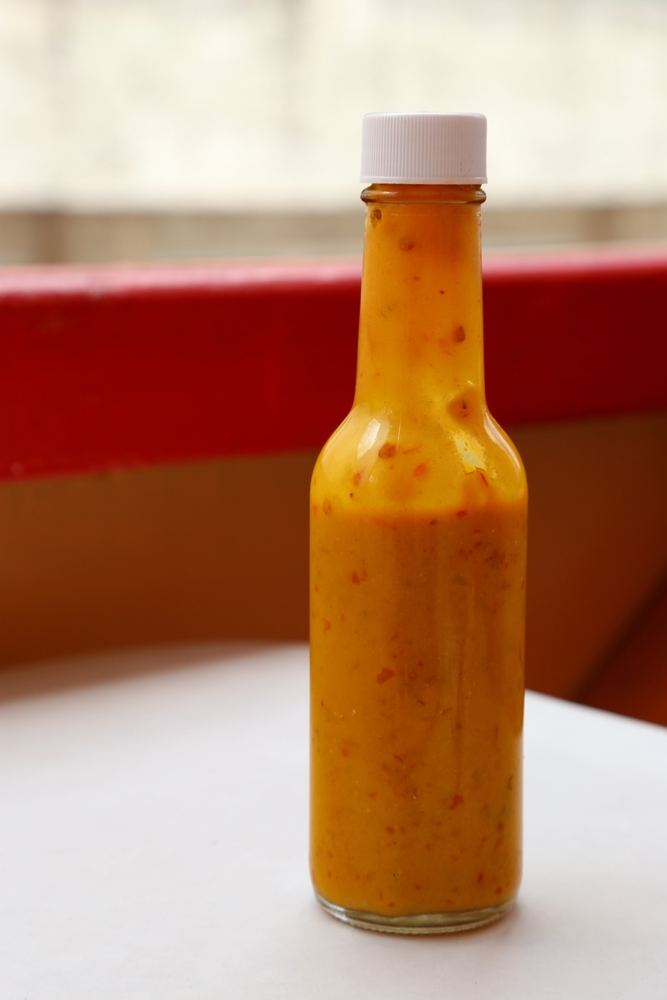

Scotch Bonnet Peppers are fiery and fruity. It is not bitter like its cousin, the habanero pepper, making it a great base for Caribbean cuisines and partner to tropical fruits. It is rich in vitamins A, B, C, and K. Scotch Bonnet pepper is also a good source of minerals such as iron, copper, magnesium, and potassium. As if that wasn’t enough, it’s also high in antioxidant carotenoids. Scotch Bonnet Peppers are highly versatile when it comes to culinary uses. This piquant pepper imparts unique flavor and color to dishes, sauces, and salsas. It can be used as a dry rub or marinade, garnish for cocktails, condiments and salsas!
So, while you may see the gates of hell while eating this hot pepper, rest assured it is contributing to your health. Be sure to wear gloves and proceed with caution when handling any hot chile pepper.
Check out our infographic below!